-
- 2014-01-13
- 思想
如何编写高质量的程序
学习任何编程语言都会有一个基本的过程,开始的时候学习基本的语法,然后学习各种库,框架,开始做各种项目。在做项目的过程中,随着代码量的增加,我们会渐渐感到失去对程序的掌控能力,bug开始增加,牵一发而动全身,顾此失彼。这充分说明了编写高质量程序的重要性,这里的“高质量”主要指程序的正确性,可读性,可维护性。
什么是高质量的程序
正确性
程序正确性的重要程度无需多言,尤其在一些特殊领域,例如芯片制造业,航天业,武器制造业,对程序正确性往往有着极其严格的要求,因为一旦程序出错,代价往往是巨大的。在这些领域,需要使用形式化方法(formal methods)来自动验证程序的正确性,也就是说你需要证明程序的正确性,而不仅仅保证程序在大多数情况下是正确的。在其它领域,对正确性没有这么高要求,形式化方法也不适用,但是我们还是需要使用其它手段,例如测试,code review等等来保证软件的正确性。
可读性
可读性可以帮助程序作者理清思路,思路清晰后,程序不容易出错。另外,其它程序员在维护你的代码时,更容易理解你的意思,方便修改bug,方便扩展。
不要浪费自己的时间,更不要浪费别人的时间。
可维护性
这里的可维护性主要指程序应对变化的能力。程序在完成基本功能后,可能会发生各种改变:用户需求变了,性能达不到要求需要重新实现算法,等等。一旦程序的一个点发生改变,其它点如果也需要同时手动改变,那么程序会变的不可控制,出bug的机会会增加。想像一下,我们的程序是一个盒子,在添加新功能时,如果只需要把新模块插到一个地方,新模块就可以被系统使用,这样的程序可维护性是很高的。但是如果添加新功能时,需要把原来的程序盒子拆开,其它模块也需要相应修改,才能加入新模块,这样的程序可维护性就很差。
Read More ... -
- 2013-11-21
- 源代码阅读
web.py 项目之 googlemodules
项目说明
项目来自 webpy.org, 这是一个真实的在线上运行的 项目: Google Modules, 可以上传,下载, 一些模块,还有一些评分,打标签等等功能。(不过这网站挺奇怪的。。。)
目录树
src/ ├── application.py ├── forum.py ├── config_example.py ├── INSTALL ├── LICENCE ├── app │ ├── controllers │ ├── helpers │ ├── models │ └── views ├── app_forum │ ├── controllers │ ├── models │ └── views ├── data ├── public │ ├── css │ ├── img │ │ └── star │ ├── js │ └── rss ├── scripts └── sql 18 directories终于遇到个稍微大一点的项目了,要好好看看。
从目录上看,整个项目分成两个部分,app 和 app_forum,每个部分都使用了 典型的MVC结构,将app分成 controllers, models, views 三大部分。
另外,网站使用的 css, js 文件,图片,也都统一放在了public目录下。
INSTALL 文件描述了如何安装部署项目, 包括在哪里下载项目,哪里下载web.py,如何 配置 lighttpd, 如何配置项目。
config_example.py 文件给了一个配置文件模板,按自己的需要修改其中内容,最后 把文件名改为 config.py 就可以了,其中包括对数据的配置,调试,缓存的开启等等。
LICENCE 文件描述了项目使用的开源协议: GPLv3。
项目使用的脚本放在scripts目录下,创建数据库使用的文件放在了sql目录下。
代码统计
先看看代码统计
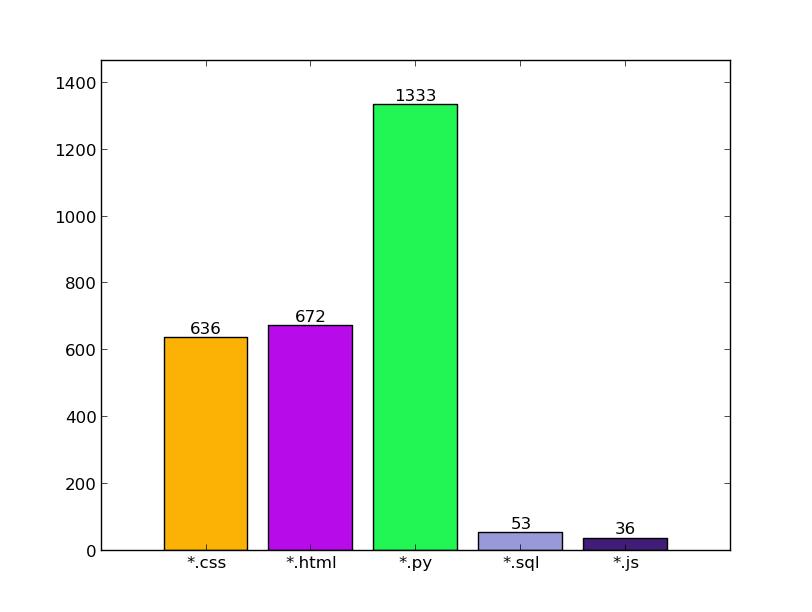
application 模块
application.py
#!/usr/bin/env python # Author: Alex Ksikes # TODO: # - setup SPF for sendmail and # - emailerrors should be sent from same domain # - clean up schema.sql # - because of a bug in webpy unicode search fails (see models/sql_search.py) import web import config import app.controllers from app.helpers import custom_error import forum urls = ( # front page '/', 'app.controllers.base.index', '/page/([0-9]+)/', 'app.controllers.base.list', # view, add a comment, vote '/module/([0-9]+)/', 'app.controllers.module.show', '/module/([0-9]+)/comment/', 'app.controllers.module.comment', '/module/([0-9]+)/vote/', 'app.controllers.module.vote', # submit a module '/submit/', 'app.controllers.submit.submit', # view author page '/author/(.*?)/', 'app.controllers.author.show', # search browse by tag name '/search/', 'app.controllers.search.search', '/tag/(.*?)/', 'app.controllers.search.list_by_tag', # view tag clouds '/tags/', 'app.controllers.cloud.tag_cloud', '/authors/', 'app.controllers.cloud.author_cloud', # table modules '/modules/(?:by-(.*?)/)?([0-9]+)?/?', 'app.controllers.all_modules.list_by', # static pages '/feedback/', 'app.controllers.feedback.send', '/about/', 'app.controllers.base.about', '/help/', 'app.controllers.base.help', # let lighttpd handle in production '/(?:css|img|js|rss)/.+', 'app.controllers.public.public', # canonicalize /urls to /urls/ '/(.*[^/])', 'app.controllers.public.redirect', # mini forum app '/forum', forum.app, '/hello/(.*)', 'hello', # site admin app # '/admin', admin.app, ) app = web.application(urls, globals()) custom_error.add(app) if __name__ == "__main__": app.run()可以看出,这是 application 部分的入口,这个模块仅仅是定义了各个请求的处理方式, 并完成程序的启动,所有的实现均不在这里出现,而是通过
import导入,特别需要 注意urls最后定义的/forum和/admin使用了子程序,而不是通过之前的字符串 实现映射。还需要注意对静态文件,即css,js,img,rss文件的单独处理。所有这些都与之前分析过的那些小项目不同,回想起我之前写的 BlogSystem, 所有的处理实现都放在 同一个文件中,导致最后一个文件居然 700多行,真是让人潸然泪下。。。 而且之前也不知道使用子程序,所有处理都堆在一起。看来读完这份源代码,真应该重构一 下了。
app 模块
app/ ├── models # 数据模块,MVC中的 M ├── views # 显示模块,MVC中的 V ├── controllers # 控制模块,MVC中的 C └── helpers # 辅助模块,实现辅助功能 4 directoriescontrollers 模块
controllers/ ├── base.py # 对基本页面,如网站主页,关于网页,帮助等的处理 ├── all_modules.py # 显示全部模块 ├── module.py # 对模块页面的处理 ├── search.py # 对搜索模块功能处理 ├── submit.py # 对提交模块的处理 ├── author.py # 查看模块作者信息 ├── cloud.py # 对标签云页面进行处理 ├── feedback.py # 处理反馈信息 └── public.py # 对静态文件的处理这个模块主要是对请求处理的实现,在
urls里定义的那些映射关系, 很多被映射到这里。实现过程中,调用 models 模块对数据操作,再送入 views 模块通过模板引擎显示数据内容。
models 模块
models/ ├── comments.py # 对评论数据的处理 ├── modules.py # 对模块数据的处理 ├── rss.py # 对 rss 订阅的处理 ├── sql_search.py # 对搜索的数据处理 ├── submission.py # 对用户提交内容的处理 ├── tags.py # 对标签内容的数据处理 └── votes.py # 对用户投票的数据处理这个模块直接调用 web.py 的db模块对数据库进行操作,对数据库的连接在 config.py 中 已经完成。这里完成数据的获取,处理,返回。可以看出,对不同种类的数据又分成了 很多小的模块。
Read More ... -
- 2013-11-18
- 源代码阅读
web.py 项目之 blog
目录树
src/ ├── blog.py ├── model.py ├── schema.sql └── templates ├── base.html ├── edit.html ├── index.html ├── new.html └── view.html 1 directory, 8 files项目说明
项目来自 webpy.org, 主要实现一个基于web的博客系统,实现了基本的增删查改。
结构分析
控制模块
控制模块包括 blog.py
Read More ...""" Basic blog using webpy 0.3 """ import web import model ### Url mappings urls = ( '/', 'Index', '/view/(\d+)', 'View', '/new', 'New', '/delete/(\d+)', 'Delete', '/edit/(\d+)', 'Edit', ) -
- 2013-11-17
- 源代码阅读
web.py 项目之 todolist
目录树
. └── src ├── model.py ├── schema.sql ├── templates │ ├── base.html │ └── index.html ├── todo.py 2 directories, 8 files项目说明
项目来自 webpy.org, 主要实现一个基于web的 todolist,就是可以添加删除一些任务。 非常简单
结构分析
控制模块
控制模块只有todo.py
Read More ...""" Basic todo list using webpy 0.3 """ import web import model ### Url mappings urls = ( '/', 'Index', '/del/(\d+)', 'Delete' ) -
- 2013-11-14
- 源代码阅读
web.py 项目之 skeleton
skeleton 是 web.py 官网上给出的一个最简单的项目结构示例。
目录树
. └── src ├── code.py ├── config.py ├── db.py ├── sql │ └── tables.sql ├── templates │ ├── base.html │ ├── item.html │ └── listing.html └── view.py 3 directories, 9 files结构分析
控制模块
#code.py import web import view, config from view import render urls = ( '/', 'index' ) class index: def GET(self): return render.base(view.listing()) if __name__ == "__main__": app = web.application(urls, globals()) app.internalerror = web.debugerror app.run()code模块作为入口:- app 的创建与启动
- url 与 处理类的映射与处理入口
但是,具体的处理并不在这里实现。而是放在了
view模块中。这一模块是MVC中的C吗?显示模块
#view.py import web import db import config t_globals = dict( datestr=web.datestr, ) render = web.template.render('templates/', cache=config.cache, globals=t_globals) render._keywords['globals']['render'] = render def listing(\**k): l = db.listing(\**k) return render.listing(l)从这里可以看出
view模块- 与模板关联
- 从数据库中取数据,然后发给模板
我们再来看看模板:
<!-- templates/base.html --> $def with (page, title=None) <html><head> <title>my site\ $if title: : $title\ </title> </head><body> <h1><a href="/">my site</a></h1> $:page </body></html>base.html是所有模块的公共部分,每个模块只需要提供 它的page,即内容就可以了。<!-- templates/listing.html --> $def with (items) $for item in items: $:render.item(item)这一模块是MVC中的V吗数据操作
数据库操作分三部分
- sql/tables.sql 数据库表定义
- config.py 数据库连接
- db.py 数据库操作
/* tables.sql */ CREATE TABLE items ( id serial primary key, author_id int references users, body text, created timestamp default current_timestamp );#config.py import web DB = web.database(dbn='mysql', db='skeleton', user='root', pw='xx') cache = False# db.py import config def listing(\**k): return config.DB.select('items', **k)这是MVC中的M吗这是 web.py 中最基本的一个项目结构。应该是使用的MVC设计模式。但是 因为程序本身不大,还体会不到 MVC 的好处。
Read More ...
